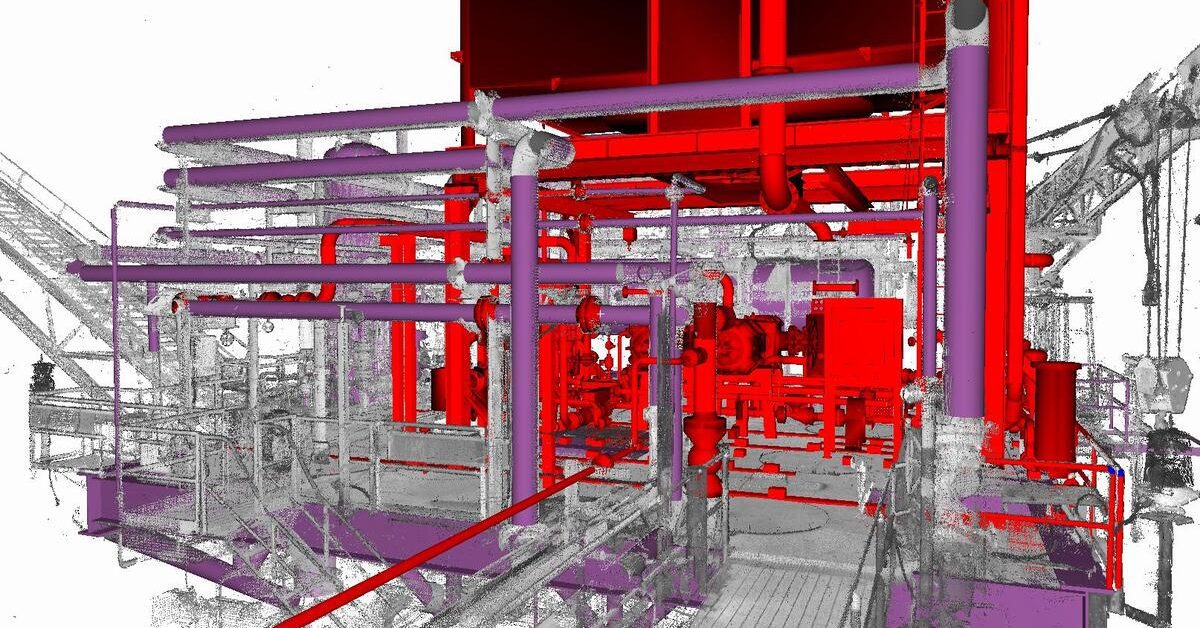
3D laser scanning is the process of making accurate and precise digital models of real-life objects, people, or spaces. 3D laser scanning can be used for 3D printing or for projects that need a portable, digital copy of something that can be annotated or adapted.
For example, 3D modeling is used in architectural and construction projects because you can scan an existing building and digitally annotate and adapt it to have a visual aid for how the finished product will look. 3D models are also great for education. For example, a 3D model of the human body can be used to help teach human anatomy.
Because 3D models are so useful, the 3D laser scanning process is important to learn, but not many people know how it works. In this article, we’ll give you all the details about how to try 3D laser scanning for yourself.
How Do 3D Laser Scanners Work?
3D laser scanners work by creating “point clouds” on an object’s surface. A point cloud is a big collection of individual points plotted on an object that relays data that represents objects or space.
Using laser technology, these lasers scan a real object, person, or space, and identify tons of tiny individual points which eventually make up the point cloud. This is used to detect the shape of the item and transfer the data to create a digital, three-dimensional model.
3D laser scanning is accurate and can detect a real object’s size, exact shape, and even color and then creates an exact digital replica.
How Accurate is 3D Laser Scanning?
The accuracy of 3D laser scanning can be spot-on, it just depends on the quality of your scanner and how confident you are about scanning. There are two types of 3D laser scanning accuracy types: volumetric accuracy and single scan accuracy.
Single scan accuracy is the accurate scan of one individual object. Volumetric accuracy is used when multiple scans are layered and merged into one new 3D model.
In general, most scanners will give you a highly accurate representation of the object, building, or person you’re scanning. Construction workers are even able to use 3D models of projects for digital walk-throughs and accurate measurements.
The 3D model should provide you will all the information you need about the existing object so that colleagues or clients that don’t have access to the object or building can see an accurate version of it.
While most modern 3D scanners are high performing and easy to use, getting an accurate 3D laser scan depends on three factors:
- Temperature (a 3D laser scanner will perform differently depending on its temperature)
- Calibration (a 3D laser scanner works best if you calibrate it regularly)
- The person performing the scan (some people are more experienced and will generally make more accurate 3D scans)
If you’re making sure you pay attention to all of these, your 3D scanner should be performing at maximum capacity for the most accurate scanning possible.
Is LiDAR the Same as 3D Laser Scanning?
LiDAR is a type of 3D scanning, but there are lots of other types of well. The term LiDAR was originally made up of the words light and radar but is now also used as an acronym for “laser imaging detection and ranging.”
LiDAR is a popular type of 3D scanning and gives some of the most accurate results compared to other 3D scanning methods. While LiDAR is 3D scanning, there are other types of 3D scanning so it wouldn’t be accurate to say that LiDAR and 3D scanning are the same thing.
What Are the Types of 3D Laser Scanning?
Depending on what you want to scan and digitize, there are different methods you can use. The three most popular types of 3D laser scanning are LiDAR, digital photogrammetry, and structured light 3D scanning.
They’re all accurate and efficient in their scanning processes, but they have different strengths and weaknesses so you’ll have to choose which one works best for you. Let’s take a closer look.
LiDAR
LiDAR is a common form of 3D laser scanning used to analyze objects, landscapes, people, and structures to help in the creation of a digital twin.
LiDAR uses a more direct laser than other forms of laser scanning, so the results are usually more accurate than if you were to use other methods. It works by calculating the amount of time it takes for light beams to hit the surface of the object or structure you’re scanning and reflect back to the laser.
LiDAR can also analyze the type of surface you’ve scanned and provides more detailed information about it, which is why LiDAR is useful for landscape surveying. It creates accurate maps and can pick up on differences in elevation, land type, and the presence of vegetation. LiDAR sensors are used in drone surveying to create 2D and 3D maps of the surveyed area.
LiDAR can be used to scan a lot of different things. It’s been used to map out entire cities, aid NASA in space travel, generate accurate floorplans for architectural work and environmental protection, as well as to identify flood risks, coastal erosion, and carbon stocks in forestry.
LiDAR is typically used for bigger projects because it layers multiple scans to create complete and accurate 3D models of massive areas. Although LiDAR is the most accurate form of 3D laser scanning and is capable of large projects, it’s the more expensive choice.
Digital Photogrammetry
Digital photogrammetry is a scanning process that takes measurements of objects in a photograph. It analyzes photographs or videos taken from different points of view and uses photogrammetric software to figure out the scale and spatial relationships.
By combining multiple images, photogrammetry can create a 3D model. The more precise the original photographs are, the more accurate the final product will be. Digital photogrammetry is used to turn pictures into maps. Architects, geologists, and engineers use this process to create topographic maps or point clouds.
There’s a wide variety of photogrammetry software out there, but scanners that use digital photogrammetry systems are usually more simple than LiDAR technologies.
via Pixabay
Structured Light 3D Scanning
Structured light 3D scanning measures the three-dimensional shape of an object using projected light patterns and cameras. The light from the scanner projects black-and-white patterns onto the object that’s being scanned. The patterns get distorted on the object, which allows its shape to be identified.
The scanner can then figure out the object’s surface information and calculate it into a 3D scan. If you want a 3D model of the whole object, you’ll need to scan the object from every side and then merge the scans to form a 3D model.
Is LiDAR Best for 3D Scanning?
In general, yes, LiDAR scanning is best for 3D scanning, especially for larger projects. It scans and calculates the area accurately and can be used for a lot of different purposes, which means it’s the most versatile form of scanning available.
Other methods are also accurate, but better suited for different types of scanning projects. Structured light works well for the 3D scanning of objects and detecting specific shapes, sizes, and textures, while digital photogrammetry is great for measuring images or detecting differences in landscape terrains.
LiDAR will provide the most accurate scan and can handle big projects that can help with global developments, like space and environmental projects.
What Is 3D Laser Scanning Used For?
One of the most popular uses for 3D scanning is creating three-dimensional models of people or objects that can be used for educational purposes or building projects. Using all three scanning methods respectively, 3D scanning can be used for pretty much anything.
The creation of 3D models can be handy for architects, engineers, and construction workers to help with the planning and development of construction projects.
By using 3D scanning technology on landscapes, geologists and environmentalists can learn more information about a specific piece of land. Because 3D scanning is used with drones a lot, no one has to walk the entire area to identify what type of land is in the area and decide if that land needs to be protected by law.
The process of 3D laser scanning is a valuable resource in our mission to help the environment because it helps us to map flood risks and monitor erosion.
It’s not only construction and education that benefit from 3D scanning—it can be even more useful to help preserve and protect fragile objects and fossils. This is especially useful in the field of archaeology. This type of scanning and printing is used to store digital replicas of rare and delicate historical artifacts.
via Pixabay
From tiny objects like coins, tools, and ornaments to larger discoveries like dinosaur bones, 3D scanning and printing can help us get a closer look without the chance of breaking or altering the actual object itself. This way, we can protect ancient discoveries while still allowing us to learn everything we can about everything we find.
This is also used by museums, which would benefit the most from having digital copies of their exhibitions to help keep the originals safe.
If an item is found already damaged, the technology used in the 3D scanning process can detect patterns on it and help digitally restore it so archaeologists can see what it looked like originally.
This same technology is even used on larger projects and helps predict what historical buildings used to look like based on the scan of their ruins.
Paleontologists can also use 3D scanners to look closely at fossils and bones found and get a better idea of what animals looked like and how they lived. This technology can help us learn more so we can make better technology in the future.
Final Thoughts
Although LiDAR technology is more expensive, if you’re looking to get more accurate scans on larger projects, it’s worth investing in. With three different types of 3D laser scanning to choose from, you can find the best type of scanner for your project. Make sure to research each scanning method to see which one would work best for you before you buy a scanner.
There are tons of uses for 3D laser scanning, and it can be used for anything from the preservation of historical artifacts to the production of NASA technology. The discovery of 3D laser scanning has been a huge step in the development of our society’s technologies and has helped some of the world’s biggest companies make some pretty amazing discoveries.