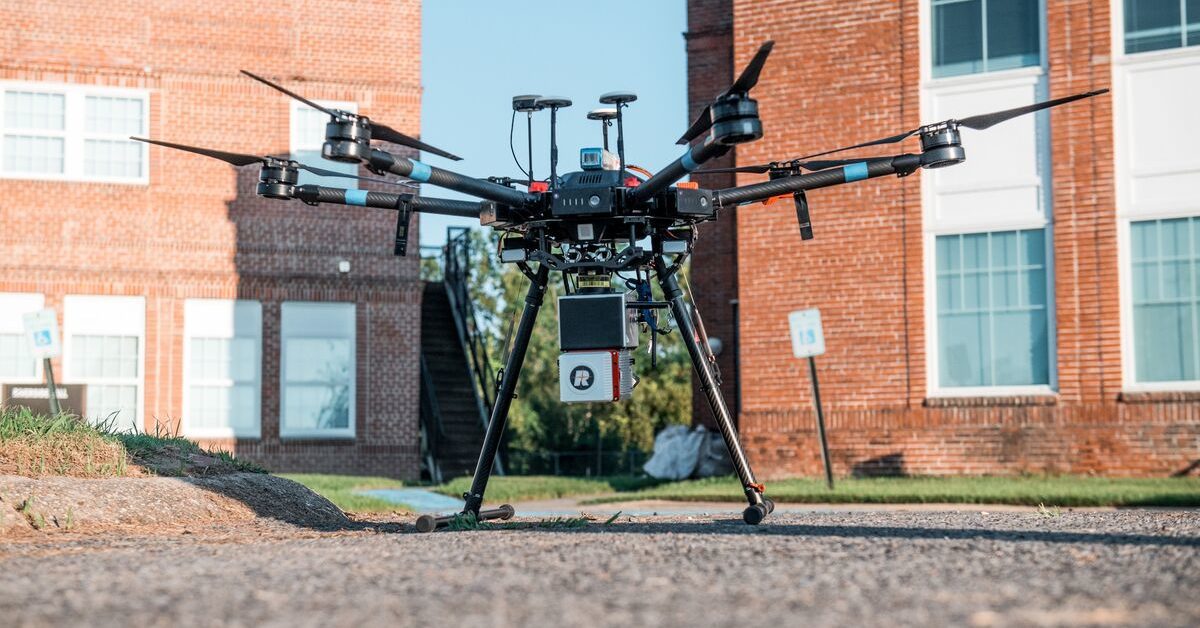
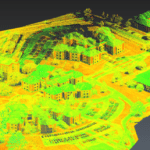
LiDAR is a remote sensing technology that helps to create three-dimensional models of dynamic scenes for surveying, mapping, autonomous driving cars, and more.
LiDAR uses lasers to measure elevations and distances of moving as well as stationary objects and allows for extremely precise measurement.
These sensors use LiDAR technology to easily map distance, as well as the shape and structure of any object. A LiDAR sensor is a device that emits laser beams toward an object. The sensor then uses the reflected light rays to calculate the distance between the object along with the shape and size in a precise 3D model.
What are LiDAR Sensors?
LiDAR sensors measure the distance between objects using pulsed laser beams. They are used to determine the distance and orientation of objects in the vicinity. A LiDAR sensor has a light emitter and a receiver.
The emitter sends pulses of light into the environment, which bounce off objects and are detected by the receiver. The receiver then measures the time since the pulses were broadcast. It provides a highly accurate, real-time 3D map of the surrounding environment.
This type of sensor is an important piece of technology used in modern car navigation systems. These devices also work by scanning the surrounding area to detect obstacles and hazards. They use a series of pulses to pinpoint the location of an object. The data produced by the scanners are used by a computer algorithm to create a complete picture of the surroundings of a vehicle.
What is the Purpose of LiDAR Sensors?
The main purpose of a LiDAR sensor is to determine distance or range from an object, and map the shape, size, and structure of an object. Laser light is used to measure the distance between the LiDAR sensor and the object. The sensor device is designed in such a way that it measures the time it takes for the light to return back to the receiver. The time is then used in a formula to calculate the distance.
LiDAR sensor is a type of remote detection and ranging device that uses laser pulses instead of radio waves. By measuring the time between a laser pulse and the reflected laser pulse, LiDAR sensors can calculate the distance to objects.
Using the speed of light, they can even identify objects at night, making them very versatile. Most camera-based systems need a certain amount of light to function, which diminishes the effectiveness in low-light situations.
LiDAR sensors are also used to map the shape, size, and structure of objects. This data can help the sensor create a precise and accurate digital 3D image of the areas. LiDAR sensors can be used to measure areas on the earth’s surface as well as under the water (to a certain depth). LiDAR sensors are versatile, as you can use them for airborne, terrestrial, mobile, and other applications.
What are the Benefits of LiDAR Sensors?
There are many benefits of using LiDAR sensors. Some of the benefits of LiDAR sensors are their accuracy, speed, wide range of applications, ability to detect smaller objects, and ability to work in a wide range of weather/light environments.
-
Accurate
LiDAR sensors are an active remote sensing system that uses pulsed lasers to map the environment. The technology uses “time of flight” measurements to obtain the distance traveled by a laser and it is extremely accurate. The short wavelength helps to map even the smallest object. Using LiDAR, you’ll get accurate 3D images with this technology.
-
Faster
One of the benefits of using a LiDAR sensor is its high speed. It receives data from laser pulses at an incredible pace. As a result, the technology is faster and more accurate than some of its alternatives. The inner processor saves the reflection points of lasers to form a 3D map of the environment, which allows for a precise map, quickly.
-
Lots of Applications
LiDAR sensors are composed of a laser source and detector. This technology can be used in many different locations and purposes. It also has less common uses, such as measuring atmospheric gases and the density of various pollutants. It can also be used in a wide range of locations, environment-wise.
-
Automated Functionality
LiDAR sensors use an automated process without any human intervention. It is more efficient in surveying and mapping as the data is collected automatically, and is not reliant on human input. This is because the sensor automatically detects objects and creates the 3D images.
-
Detects Smaller Object
Adapted from laser systems, LiDAR technology can detect small objects. The short wavelength will help you to detect even the smallest objects, unlike radar which is more useful in detecting larger objects.
-
Weather/Light Independent
Another benefit behind LiDAR technology is that the sensor detects objects regardless of what the weather is like. You can use these sensors at night in low-light conditions as well as under the water (in very specific situations!), since it is not dependent on weather and light.
Again, the sensors work underwater to a certain extent. There are many limitations when collecting information underwater, which we will go over.
How do LiDAR Sensors Work?
LiDAR sensors help to measure the distance between two points. It consists of three parts, a laser, scanner, and GPS receiver. All these three parts work simultaneously to easily detect objects, and collect incredibly valuable information on their surroundings.
-
Laser
The laser in the LiDAR sensor emits pulsed light waves towards the object. These light pulses reflect back from the surface, which are then captured by the scanner.
-
Scanner
The emitted light will reflect off the object and will return back to the sensor. The scanner in the sensor is calibrated to detect the reflected light waves.
-
GPS Receiver
Once the light is detected by the scanner, the GPS receiver in the device will calculate the distance that the light has traveled from the device. It will measure the time taken by the light to refract and reach back, thereby creating a detailed map of the position and space of the objects.
What are the Limitations of LiDAR Sensors?
Even though LiDAR sensors are extremely useful, they have some disadvantages. Some of the limitations of LiDAR are that it’s expensive, can be inaccurate at certain water depth levels, it takes a lot of computing power, and the technology can malfunction.
-
High Operating Cost
LiDAR technology has a high operating cost, which varies depending on the application. And even though this technology has become more affordable over recent history, it has yet to become an incredibly affordable technology to your average end-consumer.
-
Unreliable for Water Depth
As we mentioned earlier, LiDAR does work for scanning underwater. However, its effectiveness can vary depending on the depth of that water. This is another one of its disadvantages, its dependence on the principle of reflection. High water depths and turbulent breaking waves reduce its effectiveness. The data may not be 100% accurate, as the reflection will be affected by water depth.
-
Required Large Amount of Computing Power
LiDAR also requires large amounts of computing power to make accurate measurements. This is part of the reason why this technology is quite expensive, and can be difficult to work into a budget.
-
Malfunctions and Glitches
Lastly, they can be unreliable at high altitudes and are prone to system malfunctions and software glitches. When the light of a LiDAR system can’t penetrate certain environments, such as thick vegetation or dense forest, it can lead to glitches and malfunctions.
What is the Range of LiDAR Sensors?
The current range of LiDAR sensors varies from system to system. There are shorter-range LiDAR sensors, as well as long-range LiDAR sensors. The standard range of a 3D LiDAR sensor is 250 meters, but the range of LiDAR sensors is anywhere from just a couple of meters away to 1,000m away.
What are LiDAR Sensors Used For?
In a nutshell, LiDAR sensors are used for mapping the range of objects and creating a 3D representation of surroundings. As light passes through objects, some of it bounces off of the surface, and some disperses throughout the environment.
When light bounces off the surface, and back to the LiDAR sensor, it measures the amount of time it takes to return to the sensor, and that data has a wide range of applications.
As we’ve discussed, it can be used to map roads, surveying, and to create 3D maps. LiDAR sensors are extremely versatile and can be used for a variety of applications. Here are some common uses of LiDAR sensors
-
LiDAR sensors for autonomous cars
The LiDAR sensor is a device that acts as the eye of an autonomous car. It continuously fires laser pulses that collide with objects in front of the vehicle. The reflected light creates a point cloud that a computer then uses to construct an animated 3D representation of the environment around the car. This technology is perfect for autonomous cars.
A main advantage of LiDAR technology is its 360-degree horizontal field of view. A human driver can’t see around every corner, which makes a high-resolution, 360-degree view essential. The lasers detect the speed of light, distance, and direction of travel. The sensors are also used to monitor distances between cars, obstacles, and pedestrians all around the vehicle.
-
LiDAR sensors for aircraft
LiDAR sensors can be used to improve the accuracy of flight maps. The technology is currently available for many types of aircraft and is being used for commercial flights. It has been used in space flight since the Apollo program. Aerospace LiDAR is a type of laser scanning technology that enables aerial surveys.
It works by sending a pulse of light through a circular lens, which will bounce off any objects in its vicinity, and return back to the aircraft. This technology was originally developed to map the terrain beneath an airplane.
Aerospace LiDAR is a method of measuring the density of aerosols and other elements in the atmosphere. The technology uses patented UV detection methods to measure turbulence, clear air, and aerosols.
-
LiDAR sensors on cell phones
LiDAR sensors are also becoming incredibly popular in today’s smartphones. While the initial hype centered around the iPhone, LiDAR has many other applications, including augmented reality and environment recognition. Apple has already used LiDAR technology for the FaceID and ARKit features of its iPhones.
Another large cell phone company using LiDAR is Google, who recently announced Project Soli, which uses a radar chip (the cousin of LiDAR), instead of a liquid crystal display. Ultimately, this technology is making smartphones more advanced and exciting for consumers. With this new tech, copmanies are figuring out innovative ways to bring new creative apps and services to the mobile market.
-
LiDAR sensors for drones
Another application for LiDAR is on drones, for a variety of purposes. LiDAR sensors are used, together with drones, to perform aerial surveys of tree populations. These surveys can be used to determine the health of forests and assess storm damage. LiDAR sensors can also be used to map an entire farm’s acreage utilizing a drone.
This can help farmers reduce their costs associated with irrigation and crop production. The drone’s high resolution and accuracy provides precise data of large fields, fairly quickly. LiDAR drones are also used in archeology, which can be used to map ancient artifacts.
-
LiDAR sensors for mapping
One of the most common uses of LiDAR sensors for drones is in mapping. They can be used for a number of applications, including detecting damage to utilities, pipelines, railroad tracks, and other infrastructure.
LiDAR can also be used in mapping biodiversity. A large amount of species diversity is based on the diversity of its habitat. Using LiDAR to map vegetation and forests is an incredibly effective way to assess the biodiversity of a large space. This technology has evolved to provide detailed information about vegetation and forest structures.
Another application of LiDAR in mapping is flood mapping. The lasers of a LiDAR sensor can be used to detect water levels in rivers and lakes, which allows for detailed maps of the region, and can help city planners to assess risk.
LiDAR is also used in the construction industry for mapping. Construction companies can use land mapping via LiDAR to produce realistic images of vegetation and trees on their construction sites.
On the flip side of the environmental coin, there are many environmental applications of LiDAR as well. LiDAR can be used for the monitoring of coastal erosion and for many purposes within environmental mapping.
What are LiDAR Sensors Made of?
The technology behind LiDAR is relatively simple… in theory. It works by emitting light sources at a target and measuring the speed of the reflected light. The difference between the return times of the lasers and the distance traveled is then used to produce a digital 3D representation of the object. A LiDAR sensor is made of a laser source, a scanner, and a detector. The sensor is made of water-resistant material. Here are the parts that make up a complete LiDAR sensor.
-
Light Source
This is the part where the laser or LED light is emitted from, which is in pulses.
-
Scanner
This uses an oscillating mirror or lens to emit light. The reflected light is then focused on the detector with the help of the lens.
-
Photodetector
This consists of a solid-state photodiode, which receives the light and then processes it electronically to produce data.
-
Positioning/Navigation System
This part helps to determine the exact location of the sensor by using a GPS system. This part is only required in the mobile LiDAR system.
Companies That Make LiDAR Sensors
There are multiple companies in the LiDAR sensor business, spanning different technologies and areas of market focus. Here are a few of the top businesses to look out for in the LiDAR sensors market.
-
Velodyne Lidar Inc.
Founded in 1983, Velodyne Lidar Inc. is a pioneer in the Lidar space, and can’t be left off of any list of LiDAR sensor manufacturers.
-
Lumotive
Lumotive, which was founded by Bill Gates, has developed a LiDAR system that can guide autonomous vehicles. It has patented beam-steering technology to increase vehicle stability.
-
Waymo
Waymo, which is a subsidiary of Alphabet Inc. (just like Google), has begun manufacturing its own LiDAR sensors. The company’s product line is expected to reach a production volume of 250,000 units by the end of the year.
-
Hexagon AB
Hexagon AB is a Swedish manufacturer of LiDAR systems. They have a global presence in many different industries and have been manufacturing and selling LiDAR systems for many years.
-
Aeva
This company produces automotive-grade LiDAR sensors that have improved range, resolution, and value. Their products are backed by a long list of strategic partners and investors.
-
Sense Photonics
This San Jose-based company develops advanced 3D sensing solutions for autonomous vehicles. This company specializes in providing advanced 3D sensor solutions for automotive applications.